Right now, Bluetooth reigns as the best wireless transfer for data over short ranges.
However, Bluetooth finds has a new competitor in NFC or Near-field communication and it is gaining popularity steadily.
If you are in the business of custom mobile app development, you might be hearing a lot about NFC payment apps.
But how does this technology work and how is it any better than Bluetooth? Well, today’s your lucky day because, in this article, we will discuss NFC Vs Bluetooth.
A Brief Overview: NFC Vs Bluetooth:
Bluetooth technology has been around since 1998 and for years, it has reigned as the best technology for wireless data transfer.
It was created specifically for mobile phone usage. It works by sending low-intensity signals of around 1 milliwatt that prevents collision with other wireless device signals inside the range.
The consumption of low power also makes it perfect for applications and devices powered by batteries.
Near-field communication (NFC) is a wireless technology that matches distiches for sharing data and communication.
Data can be sent among two devices that are within 10 m of each other. Only one device can connect at a time. Data NFC transfer speed is as fast as 424 kbit/second.
Any NFC-powered device can communicate or match with powerless NFC chips.
This technology is best for money transfer and payments between two machines, gathering and sending data.
Using NFC is easy and it can be extremely beneficial. Technique-wise, it is a lot similar to Bluetooth, but it is a more dedicated, safer, and more reliable form of file and data transfer, including payments.
It is touch technology that is wireless that is particularly useful for the simple transfer of data. It sends data over radio waves (Radio Frequency Identification).
The machines have to kept close to each other to experience a fast and smooth information transfer.
Data transfer can happen between two devices powered by NFC and between two chips powered by NFC.
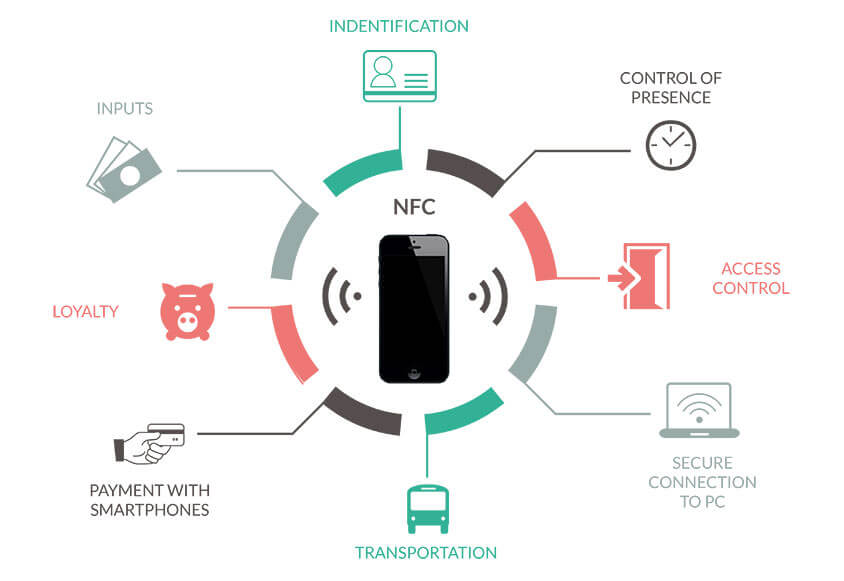
Top NFC Applications Examples:
Near-field communication has benefits for many applications where you need a brief message to be transferred over a short distance between two machines.
Here are some examples of wireless near field communication:
☛ Contacts
NFC is used for swapping contact details between phones. This offers certain security benefits like messages are harder to intercept due to the short distance.
☛ Information
NFC is used for communicating small data bits like URLs. For instance, a smart movie poster can transfer the link to a nearby shop or a video.
☛ Payments
NFC is used for quickly paying for things by touching a smart card or a mobile device to a device accepting payment.
☛ Tickets
NFC is used for tickets for transportation and events. This is an important technology for train or metro stations that manage a huge volume of people during rush hours.
☛ Identity
Multi-factor authentication is often used for secure access items like employee IDs that use NFC; Near-field communication is also often used as entry keys for things like vehicles and apartment buildings.
☛ Configuration
NFC is applied to configure things; for instance, placing your mobile phone closer to a printer to configure the entrance.
☛ Tags
NFC is used for tagging items for reasons like asset tracking.
☛ Toys
NFC is often used in toys to enable different elements to work collectively. For instance, a doll is aware of the shoes it is wearing.
☛ Feature Unlocking
NFC helps as an upgrade where features are opened when you purchase new things. A talking doll, for instance, learns a new word when you buy it a new clothing item.
☛ Games
NFC is often used in game equipment such as mobile gaming gadgets or controllers. For instance, NFC enables players to trade items in the game.
Understanding Major Difference between NFC Vs Bluetooth:
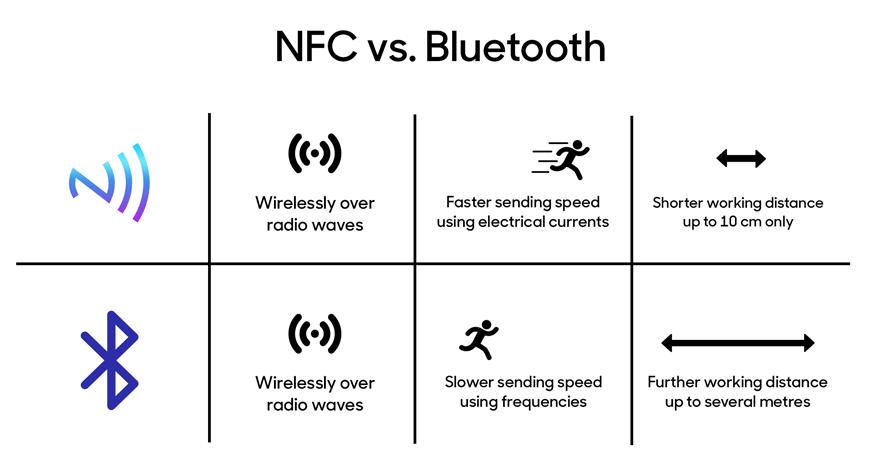
NFC has real-world benefits to offer, but how does it compare to Bluetooth-based applications?
Here, we look at NFC Vs Bluetooth:
☛ Distance
Distance is among the most important difference between Bluetooth and NFC. While both of them are short-distance technologies of wireless information communication, there is a massive difference between their capacities of transmitting and receiving.
Bluetooth’s maximum range is till 10 meters, which implies you can transact with another device powered by Bluetooth located on the other end of a room, in the adjoining room, or even over the same floor area.
NFC, meanwhile, has a very limited range—under 4 cm. Therefore, for efficient data transactions to occur, either devices or tags enabled by NFC will require to be touching or being very close to each other.
☛ Usability
NFC connections are easy to set and it does not need any authentication. You just need to turn the NFC on and bring your device close to the other NFC-enabled device and the data gets transferred instantly.
Bluetooth needs a sequential method to be performed for data transmission. Usually, you will require entering a PIN code, and configure other settings to pair devices. This makes Bluetooth usage a little time-consuming.
☛ Power Consumption
NFC is slow and has a short distance, it uses low-intensity radio transmitters, and therefore, battery life isn’t that affected. Also, NFC can be on all the time without you worrying that it’s draining the battery.
This is great news for Android App Development developers.
Bluetooth consumes low power too, but it is still a bigger chunk than what NFC consumes. If you keep the Bluetooth ON in your device, you will notice your battery charge dropping.
Therefore, when it comes to battery usage, NFC is the clear champion.
☛ Data Transfer Speed
By design, NFC is close-range and low-power, and thus, has relatively lower speeds of data transmission. NFC transfers 400 Kbit/s, which is lower than other wireless tech.
However, taking into account the particular application area NFC is created for, the speed is satisfactory.
Bluetooth consumes more power and is designed to serve over greater distances. Therefore, it has higher speeds of transmissions at 2 Mbit/s. This makes it perfect to send larger data, such as videos, music, etc.
☛ Security
As a Mobile App Development Company, your app needs to be safe to use. NFC, in this regard, wins over Bluetooth even if it has no safety measures built-in.
Due to its limited range, hackers would need to be standing in front of you if they want to intercept the near-frequency communication, and that is not very safe for the hacker’s identity, thus defeating their purpose.
This is what makes NFC safe for making payments and any other transactions that include private or sensitive data.
Meanwhile, even with authentication with PIN and other safety features, transfers over Bluetooth still face safety issues and remain defenseless to attacks.
The larger range allows hackers to intercept the signal from a distance anonymously.
☛ Multimedia
NFC does not have the scope and data transfer speed required for multimedia applications such as attaching to speakers or wireless headsets.
On the other hand, Bluetooth transmission is quick and long enough and is hence perfect for multimedia uses.
☛ Passive Tags
NFC can operate with passive Radio Frequency Identification tags. One important use of this is that you can extract data on the owner of a lost pet just by tapping your phone powered with NFC on the tag on the pet’s collar.
RFID tags can also be modified to activate specific commands, such as loading web pages.
Bluetooth does not work with passive tags, and hence, cannot be used in applications that involve their use.
The Question: NFC is better than Bluetooth?
This is not quite the right question to ask. In the debate of NFC Vs Bluetooth neither is any better or worse than the other.
Both are somewhat similar technologies with almost similar features. Both have their distinct pros and cons depending on how you use them.
For instance, if you want to share a song, Bluetooth is great while if you want a link for something, NFC is ideal. However, there are some areas where NFC is, in fact, better than Bluetooth –
- NFC consumes less power than Bluetooth, so even if you leave it on, your battery won’t be drained faster
- File sharing with NFC doesn’t need pairing, which makes it quick. Also, since there is no pairing, there are no records, which makes NFC ideal for anonymous use
- NFC can be used with NFC tags – you don’t get this with Bluetooth
- Payments are safer over NFC and Bluetooth actually doesn’t have functionality for the protection of sensitive data like bank details
Conclusion
It is obvious that NFC is a revolutionary technology, but it is not a rival to Bluetooth, especially when you can see how different their applications are.
It all depends on what you want to use either Bluetooth or NFC for. When you Hire Mobile App Developer, keep in mind your requirements and applications.